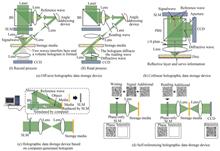
Dennis Gabor's groundbreaking contributions in the 1 940 s initially illuminated the enigmatic and potentially boundless field of holography. Over the subsequent decades, through his relentless perseverance, he continuously deepened and refined the theoretical framework of this technology. Holography, once perhaps confined to the realm of scientific fancy, gradually evolved into a pivotal tool for exploring new horizons in information storage, led by Gabor's visionary guidance. As the 1960s dawned, the rapid advancement of science and technology paved the way for Van Heerden, who, with his prescient vision, boldly foresaw the vast potential applications of holographic technology in data storage. This idea, akin to a seed, swiftly germinated and flourished with the nourishment provided by laser technology. The emergence of lasers furnished the crucial light source necessary for holographic data storage technology, thereby transitioning holographic data storage from theoretical discourse to practical implementation and gradually positioning it as a shining star in the landscape of next-generation optical storage.The unique advantage of holographic optical data storage resides in its unprecedented capacity to store information in a three-dimensional space within the recording medium. This distinctive feature allows for the parallel writing and reading of data, in stark contrast to traditional two-dimensional data transmission methods. By adopting this three-dimensional storage approach, holographic data storage technology not only vastly enhances storage capacity but also markedly boosts data transmission speed. Consequently, holographic data storage demonstrates unparalleled superiority in addressing the challenges posed by the big data era. The core of holographic data storage technology hinges on the volumetric recording of spatial light wave distributions, ushering in an entirely novel mode of data page storage. Leveraging the selective properties of thick holograms, holographic data storage facilitates parallel data processing and multiple recordings within the same medium area, resulting in faster data transmission rates and higher storage densities. This technology not only transcends the confines of traditional optical disc storage but also pioneers new avenues in the realm of data storage.To date, the domain of holographic data storage has delved into a variety of devices and technical solutions, with off-axis and coaxial systems emerging as the two most central system architectures. Furthermore, technologies rooted in computer-generated hologram and self-referencing have sequentially emerged, providing fresh momentum to the advancement of holographic data storage technology. As research continues to deepen, holographic data storage technology has made significant progress in multiple dimensions, including data recording density, data transmission rate, data storage security, environmental tolerance, and rewritable media. To further enhance the recording density of holographic data storage, researchers have proposed various innovative methods, among which multiplexing technology is key to achieving high storage density.Volume holographic data storage technology, leveraging the Bragg selectivity of volume holographic gratings, enables the storage of multiple sets of data at the same location within the storage medium, with each data page being individually readable. The implementation of this technology hinges on two primary categories of methods: spatial multiplexing and orthogonal/incoherent multiplexing. Spatial multiplexing techniques, specifically angle multiplexing and shift multiplexing, accomplish multi-address storage of information by adjusting either the angle or the relative position between the reference light and the object light. This approach effectively harnesses the storage volume, ultimately enhancing storage density and efficiency. To address the significant crosstalk noise issue in spatial multiplexing technology, researchers have introduced orthogonal/non-correlated coding multiplexing strategies for reference light. This strategy, based on the fundamental physical properties of light waves, has promoted the development of amplitude coding, phase coding, and polarization coding multiplexing technologies. By adjusting the pattern parameters of the reference light, multiple holograms can be stored in a superimposed manner, and through carefully designed grating superposition, only a specific diffraction efficiency is maximized, thereby effectively reducing crosstalk noise and enhancing the storage efficiency of the system.It is noteworthy that these multiplexing technologies do not exist in isolation but can be integrated and applied together to further promote the increase in storage density. When combined with multi-dimensional modulated data information, holographic data storage technology is expected to achieve unprecedented storage densities. Looking ahead, with the continuous progress of materials science, optical engineering, and information technology, holographic data storage multiplexing technology will continue to make new breakthroughs and contribute more to the informatization process of human society. Beyond the traditional application field of data storage, holographic multiplexing technology also exhibits broad application prospects in areas such as three-dimensional display, augmented reality, and optical communications. These emerging applications will not only further enrich the connotation of holographic data storage technology but also inject new vitality into the development of the world economy. Therefore, we have reason to believe that holographic multiplexing technology will play an increasingly important role in the future, becoming an important force in driving scientific and technological progress and economic development.
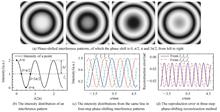
Phase-shifting Digital Holography(PSDH),which combines phase-shifting technology with digital holography, provides a fast, non-invasive, and high-precision approach for the three-dimensional morphology or refractive index distribution of microscopic objects. Compared with the off-axis digital holography, the phase-shifting on-axis digital holography makes full utilization of Spatial-bandwidth Product (SBP) of the CCD camera. The conventional phase-shifting digital holography needs to records multiple phase-shifting holograms in a step-by-step manner, from which the artifact-free phase and amplitude images of a sample can be reconstructed. To enhance the imaging speed of PSDH, parallel phase-shifting technique (or simultaneous phase-shifting technique) was proposed, with which multiple phase-shifting holograms can be obtained at the same time. In this paper, the concept and implementation of phase-shifting technologies are introduced firstly. Then, three different approaches of parallel phase-shifting, which are based on multiple CCDs, pixelated phase-mask, and parallel beam-splitting, are reviewed. Eventually, the applications of parallel PSDH in the biomedical field, air/liquid flow visualization, surface topography, micro-/nano-scale device inspection are introduced.
A nonlinear reconstruction method with a single digital hologram using deep learning was proposed for off-axis Fresnel digital hologram. Classic Fresnel diffraction integral is utilized for simulating digital holographic imaging to provide the training samples, and a deep convolution residual neural network is utilized to implement on the object image reconstruction from the recorded hologram, by learning the nonlinear mathematical mapping from the digital hologram to the corresponding object image. The results of numerical simulation experiments show that the method could directly eliminate zero-order images and twin images without fringe pre-processing procedure for extracting object term, compared with the traditional frequency filtering and four-step phase-shift techniques for achieving Fresnel digital holography reconstruction, as well as high quality reconstructed object image. It also has strong robustness to the test dateset generated with different diffraction distances using same recording reference light waveform.
In a holographic waveguide display system, the inconformity of grating parameters of input grating, turning grating and output leads to a lot of difficulties in system design and gratings fabrication process. The main condition that the turning grating should be in 60° conical mounting, on which all the gratings in a waveguide holographic display configuration have uniform grating periods, was presented by comparing the grating equations in normal mounting and conical mounting. Under this condition, a novel efficient display was proposed by using a waveguide holographic configuration with three holographic gratings of the same grating periods recorded on a single substrate and a reflector placed on the side face of the substrate. The validity of this configuration was proved by the simulation carried out by the optical design software CODE V. The coupling efficiency loss and invalid area can be dramatically reduced by the reflector on the side face, compared with the traditional configuration. Moreover, the complexity of system design and holographic manufacture can be decreased because all gratings used in the proposed design have uniform grating periods and two of them have uniform orientation. The configuration can be applied to virtual reality display or wearable display.
Background decrease method and adaptive filtering methods were proposed to solve the background removing problem in digital holographic microscopy in the in-line digital holographic microscopy.In-line digital holography microscopic system was set up, with which the digital holographic images of onion epidermis, the plant roots′ sample, the lamina stoma sample and the blood cell sample were reconstructed, respectively.In addition, the advantages of the proposed methods were demonstrated by calculating the light intensity distribution curves and the values of the contrast of images obtained with the in-line digital holographic microscope device.The results show that the backgrounds in the measured holographic interferometric fringes change with the experimental conditions and the sample itself.So that the backgrounds could be divided into three types, for each of which an appropriate method was proposed to achieve the best reconstruction image quality.The results may be helpful for reconstructing the better quality images.
A new algorithm was proposed to improve vibration-related fringes contrast for micro-vibration online detection based on time-average digital holography. First, phase change arising from the longitudinal micro-displacement of the object during vibrating process was corrected. Then phase noise caused by speckle noise was eliminated, and thus fringes pattern contrast that modulated by Bessel function was improved effectively. Finally, the amplitude distribution of the measuring surface was estimated according to Bessel function and fringe progressions. An experimental system based on time-average digital holographic interferometry was proposed for micro-vibration measurement that acoustic wave was used for excitation source. The experiment was verified by the reed that excited at the sinusoidal frequency of 0, 1 100, 2 000 and 9 000 Hz, respectively. The result based on vibration frequency of 2 000 Hz shows that the proposed method can improve vibration-related fringes contrast effectively. Amplitude of three-order zero points are 109.4 nm, 244.2 nm and 356.4 nm, and errors are 6.31%, 3.34% and 3.78%, respectively, compared with theoretical values, which demonstrate the effectiveness of the method within the allowable range.
The exposure sensitivity and polarization sensitivity of spiropyran doped polymers after the irradiation in short-wavelength range were significantly improved. Based on such properties, holographic grating recordings accompanying with a linearly polarized blue-violet beam (405 nm) in the photochromic film were performed by two coherent green beams (532 nm) for s-p formation. Under the bi-photonic action of 405 nm and 532 nm, temporal evolution of diffraction efficiency was strongly dependent on auxiliary light intensity. It was found the blue-violet irradiation plays double roles in holographic recordings: on one hand, providing the molecular orientationable merocyanine for the recording beams;on the other, disrupting the formation of refractive index gratings and reducing the conversion activity of merocyanine molecule.Taking the existence of merocyanine aggregation in the random light field of interference fringes into account, an theoretical model was established which reveals the relationship between diffraction efficiency and light-rate-constant of each molecular.The experimental results are precisely fitted with this model, the microscopic reaction mechanism of spiropyran and merocyanine molecules in polarization holographic recording was effectively explained.
In a holographic waveguide display system, the diffraction efficiency, location, and length of each ouput grating make great impact on the uniformity of output intensity and ratio of energy utilization. Generally uniformity of output intensity is decided by the diffraction efficiency distribution of each output grating, and ratio of energy utilization rests with the location and length of each ouput grating. Firstly, aming at the uniformity of central field of view, the diffraction efficiency distribution of corresponding output grating was optimized and curve fitting, and a continuous and increasing curve of efficiency distribution was obtained. Similar processing was carried out for other gratings corresponding to other FOV. Calculation results demonstrate that the uniformity of output intensity of HWDS will be improved notablely when output gratings with optimized continuous and increasing diffraction efficiency distributions are used than that of traditional output gratings with step diffraction efficiency distributions. A shifting-optimization method was proposed to optimize the location of each grating according to the size of exit pupil and usage distance, so that the ratio of energy utilization of HWDS could be greatly incereased resulted from the reduction of the invalid diffraction region.
A method for choosing angle of reference beam in computer-generated holograms based on spatial frequency analysis of principle fringe pattern was proposed. The rules for reconstructed image rightly were obtained through analyzing the spatial frequency of principle fringe pattern. The angles of reference beam in the holography reconstructed system based on spatial light modulator were computed. The holograms of one image plane with size of 22.5 mm×26.1 mm were generated at the distance of 1 000 mm when different angles of reference beam were chosen. The digital and optical reconstructed experiments were conducted respectively. The results indicate that the angle of reference beam must be chosen in the range which is from 0.893 8° to 1.398 0° in order to achieve good quality of reconstructed images. If the angle of reference beam is smaller than 0.893 8°, the reconstructed image and the conjugate image could not be separated completely, whereas the reconstructed image would overlap with the conjugate image of the next order if the angle of reference beam is larger than 1.398 0°. The experimental results validate the theoretical analysis very well.